Building an X3D World
X3D file structure
X3D files contain:
- The file header
- Comments - notes to yourself
- Nodes - nuggets of scene information
- Fields - node attributes you can change
- Values - attribute values
- Routes - connections between fields
- more …
A sample X3D file
XML Encoding
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<X3D profile='Full' version='4.0' xmlns:xsd='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xsd:noNamespaceSchemaLocation='http://www.web3d.org/specifications/x3d-4.0.xsd'>
<Scene>
<!-- A Cylinder -->
<Shape>
<Appearance>
<Material/>
<Appearance>
<Cylinder
height='2.0'
radius='1.5'/>
</Shape>
</Scene>
</X3D>
Classic Encoding
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#X3D V4.0 utf8
# A Cylinder
Shape {
appearance Appearance {
material Material { }
}
geometry Cylinder {
height 2.0
radius 1.5
}
}
Example
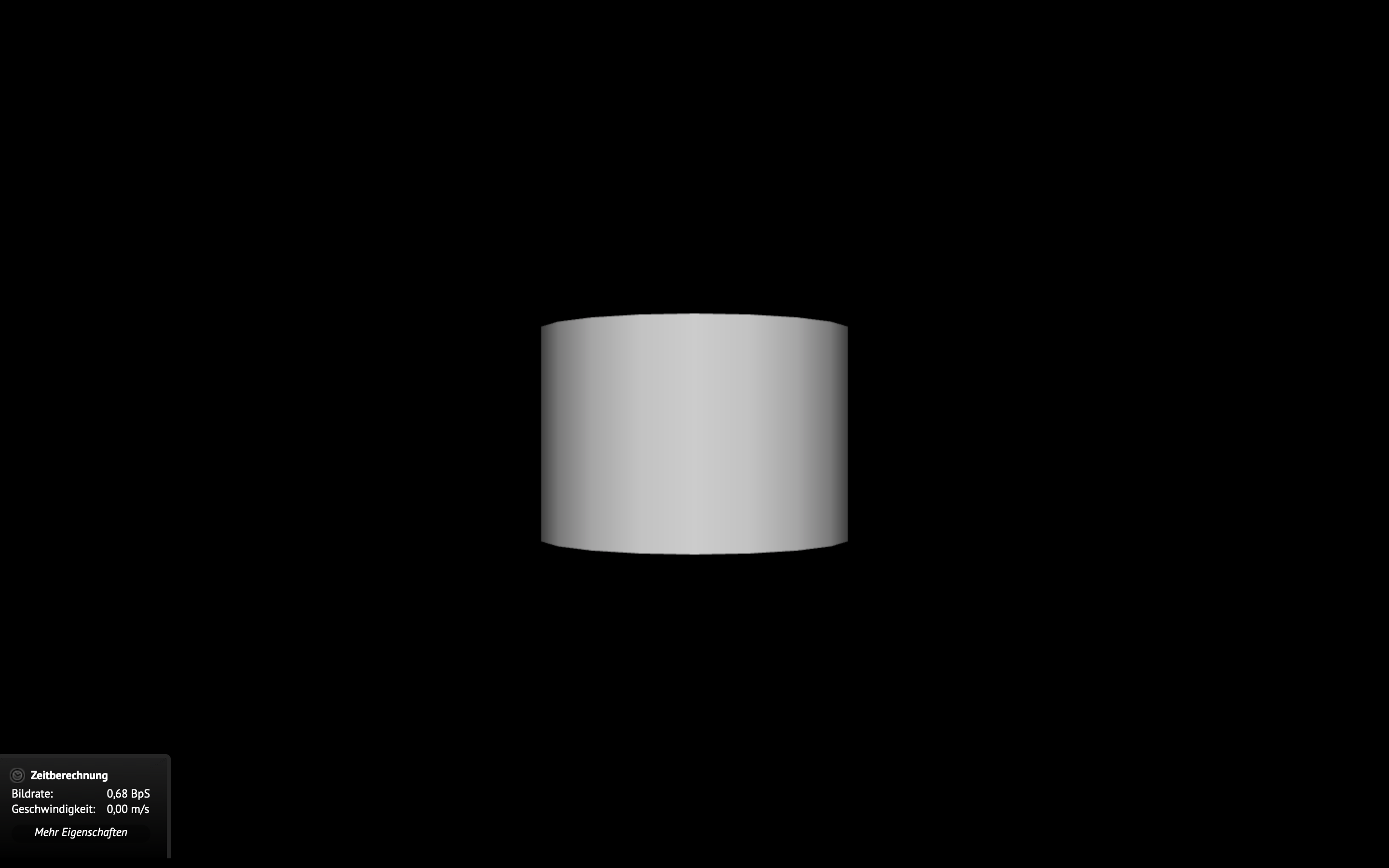
Understanding the header
#X3D V4.0 utf8
- #X3D: File contains X3D text
- V4.0 : Text conforms to version 4.0 syntax
- utf8 : Text uses UTF8 character set
Understanding UTF8
- utf8 is an international character set standard
- utf8 stands for:
- UCS (Universal Character Set) Transformation Format, 8-bit
- Can encodes up to 2,164,864 characters for many languages
- ASCII is a subset
Using comments
1
# A Cylinder
- Comments start with a number-sign (#) and extend to the end of the line
Using nodes
XML Encoding
1
<Cylinder/>
Classic Encoding
1
2
Cylinder {
}
- Nodes describe shapes, lights, sounds, etc.
- Every node has:
Using node type names
Node type names are case sensitive:
- Each word starts with an upper-case character
- The rest of the word is lower-case
Some examples:
Appearance, Cylinder, Material, Shape
Using fields and values
XML Encoding
1
2
3
<Cylinder
height='2.0'
radius='1.5'/>
Classic Encoding
1
2
3
4
Cylinder {
height 2.0
radius 1.5
}
- Fields describe node attributes
Every field has:
- A field name (height, radius, etc.)
- A data type (float, integer, etc.)
- A default value
- Different node types have different fields
- Fields are optional
- A default value is used if a field is not given
- Fields can be listed in any order
- The order doesn’t affect the node
Placing nodes
Every node has a »containerField« attribute with a default value, which is different for each node type. You can change the value if needed.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<Collision>
<Shape containerField='proxy'>
<Box/>
</Shape>
<Transform>
<!-- ... -->
</Transform>
</Collision>
Summary
- The file header gives the version and encoding
- Nodes describe scene content
- Fields and values specify node attributes
- containerField attribute can be changed.
- Everything is case sensitive
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.