Sensing the Viewer
Motivation
Sensing the viewer enables you to trigger animations:
- when a region is visible to the viewer
- when the viewer is within a region
- when the viewer collides with a shape
The LOD and Billboard nodes are special-purpose viewer sensors with built-in responses.
Sensing the viewer
There are three types of viewer sensors:
- A VisibilitySensor node senses if the viewer can see a region
- A ProximitySensor node senses if the viewer is within a region
- A Collision node senses if the viewer has collided with shapes
Using visibility and proximity sensors
VisibilitySensor and ProximitySensor nodes sense a box-shaped region:
- center - region center
- size - region dimensions
Both nodes have similar outputs:
- enterTime - sends time on visible or region entry
- exitTime - sends time on not visible or region exit
- isActive - sends true on entry, false on exit
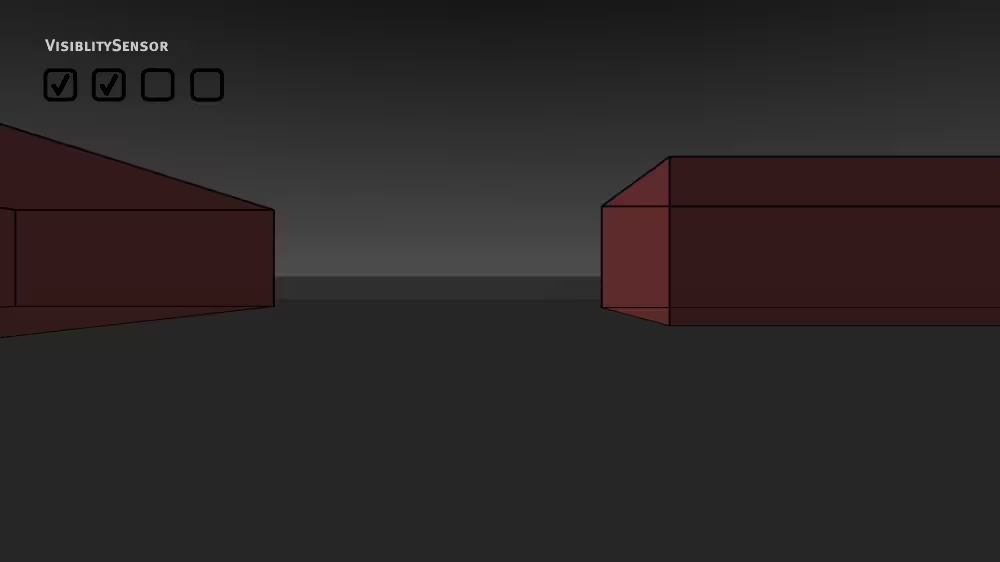
Syntax: VisibilitySensor
A VisibilitySensor node senses if the viewer sees or stops seeing a region:
- center and size - the region’s location and size
- enterTime and exitTime - sends time on entry/exit
- isActive - sends true/false on entry/exit
XML Encoding
1
2
3
4
5
<VisibilitySensor DEF='Sensor'
center='0.0 0.0 0.0'
size='14.0 14.0 14.0'/>
<ROUTE fromNode='Sensor' fromField='enterTime' toNode='Clock' toField='set_startTime'/>
Classic VRML Encoding
1
2
3
4
5
6
DEF Sensor VisibilitySensor {
center 0.0 0.0 0.0
size 14.0 14.0 14.0
}
ROUTE Sensor.enterTime TO Clock.set_startTime
Example
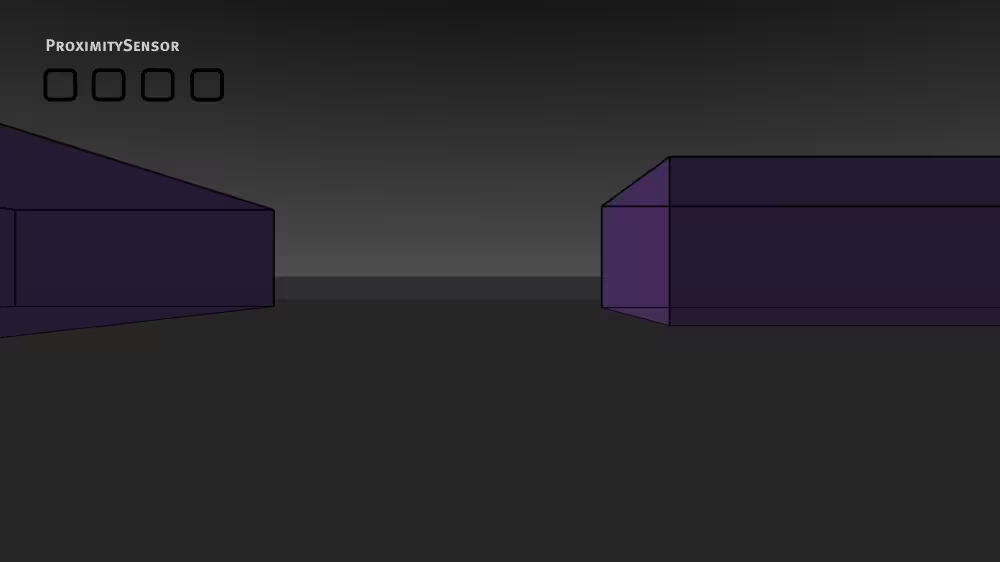
Syntax: ProximitySensor
A ProximitySensor node senses if the viewer enters or leaves a region:
- center and size - the region’s location and size
- enterTime and exitTime - sends time on entry/exit
- isActive - sends true/false on entry/exit
XML Encoding
1
2
3
4
5
<ProximitySensor DEF='Sensor'
center='0.0 0.0 0.0'
size='14.0 14.0 14.0'/>
<ROUTE fromNode='Sensor' fromField='enterTime' toNode='Clock' toField='set_startTime'/>
Classic VRML Encoding
1
2
3
4
5
6
DEF Sensor ProximitySensor {
center 0.0 0.0 0.0
size 14.0 14.0 14.0
}
ROUTE Sensor.enterTime TO Clock.set_startTime
Example
A ProximitySensor node senses the viewer while in a region:
- position and orientation - sends position and orientation while viewer is in the region
XML Encoding
1
2
3
<ProximitySensor DEF='Sensor' ... />
<ROUTE fromNode='Sensor' fromField='position_changed' toNode='PetRobotFollower' toField='set_translation'/>
Classic VRML Encoding
1
2
3
DEF Sensor ProximitySensor { ... }
ROUTE Sensor.position_changed TO PetRobotFollower.set_translation
Detecting viewer-shape collision
A Collision grouping node senses shapes within the group:
- Detects if the viewer collides with any shape in the group
- Automatically stops the viewer from going through the shape
Collision occurs when the viewer’s avatar gets close to a shape:
- Collision distance is controlled by the avatar size in the NavigationInfo node
Creating collision groups
Collision checking is expensive so, check for collision with a proxy shape instead:
- Proxy shapes are typically extremely simplified versions of the actual shapes
- Proxy shapes are never drawn
A collision group with a proxy shape, but no children, creates an invisible collidable shape:
- Windows and invisible railings
- Invisible world limits
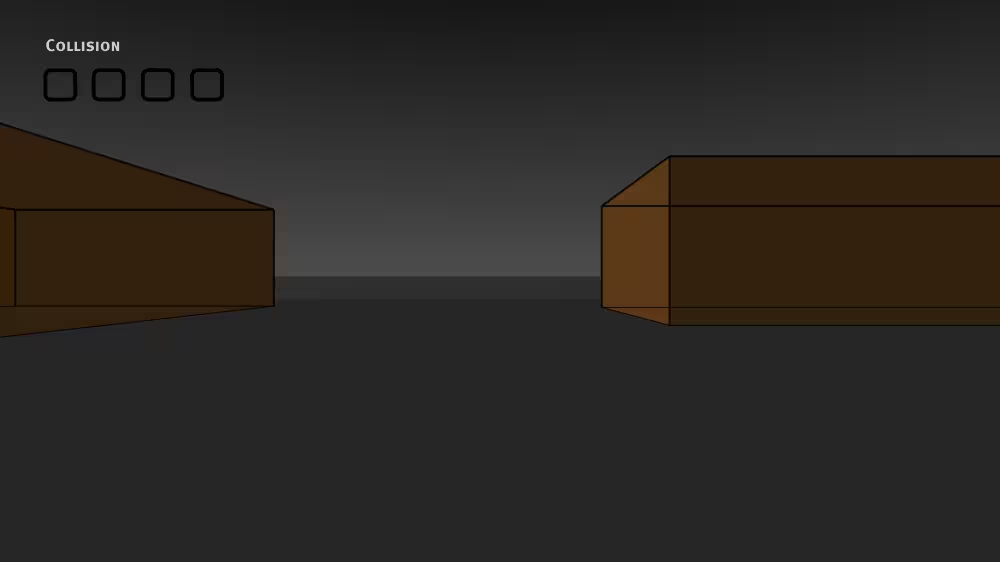
Syntax: Collision
A Collision grouping node senses if the viewer collides with group shapes:
- enabled - enable/disable sensor
- proxy - simple shape to sense instead of children
- children - children to sense
- collideTime - sends time on collision
XML Encoding
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
<Collision DEF='Collide'
enabled='true'>
<Shape containerField='proxy'>
<Box ... />
</Shape>
<!-- children ... -->
</Collision>
<ROUTE fromNode='Collide' fromField='collideTime' toNode='OuchSound' toField='set_startTime'/>
Classic VRML Encoding
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
DEF Collide Collision {
enabled TRUE
proxy Shape {
geometry Box { ... }
}
children [ ... ]
}
ROUTE Collide.collideTime TO OuchSound.set_startTime
Example
Optimizing collision detection
- Collision is on by default
- Turn it off whenever possible!
- However, once a parent turns off collision, a child can’t turn it back on!
- Collision results from viewer colliding with a shape, but not from a shape colliding with a viewer
Using multiple sensors
Any number of sensors can sense at the same time:
- You can have multiple visibility, proximity, and collision sensors
- Sensor areas can overlap
- If multiple sensors should trigger, they do
Summary
A VisibilitySensor node checks if a region is visible to the viewer:
- The region is described by a center and a size
- Time is sent on entry and exit of visibility
- True/false is sent on entry and exit of visibility
A ProximitySensor node checks if the viewer is within a region:
- The region is described by a center and a size
- Time is sent on viewer entry and exit
- True/false is sent on viewer entry and exit
- Position and orientation of the viewer is sent while within the sensed region
A Collision grouping node checks if the viewer has run into a shape:
- The shapes are defined by the group’s children or a proxy
- Collision time is sent on contact